In 2018, a multi-disciplinary team of researchers from Oxford and Newcastle, led by Professor Rutger Ploeg and Professor James Shaw, was awarded a grant of £1.7 million from the Medical Research Council (MRC) to enable the expansion of QUOD to establish a whole organ tissue bank.
This funding enabled the central QUOD clinical data, blood and urine sample, and tissue biopsy bioresource in Oxford to be augmented by systematic processing of whole-organ pancreas, heart, and lungs from deceased organ donors to collect anatomically driven mutimodal biopsies. This grant allowed QUOD to establish cross-cutting scientific platforms including state-of-the-art pathology, transcriptomics, proteomics, and light / multiplex fluorescence / EM imaging. The QUOD–PANC tissue bank at Newcastle University has archived samples from 120 donors within a searchable online Atlas, comprising normal, ischaemic, and chronically diseased pancreata. Underlying pathologies include type 1, type 2, and type 3c diabetes, in addition to chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN).
About QUOD Whole Organ Resource
The QUOD whole organ expansion programme at Newcastle University is coordinated by scientists and clinicians including Professors James Shaw, Andrew Fisher, John Dark, and Dina Tiniakos, and Dr Bill Scott. Quality-assured tissue processing is undertaken by dedicated biomedical scientists led by Minna Honkanen-Scott within the Transplant Regenerative Medicine Laboratories at the International Centre for Life. Professor Paul Johnson leads a parallel research pancreatic islet isolation programme at the University of Oxford.

QUOD Expand facilitates integration of high-quality clinical data, circulating biomarkers, and deep molecular phenotyping towards a deeper understanding of the stresses associated with organ donation and transplantation together with the mechanisms underlying tissue pathologies. The overall goal is the development of novel therapeutic strategies to optimise organ transplantation, tissue replacement therapy, and in situ endogenous tissue repair.
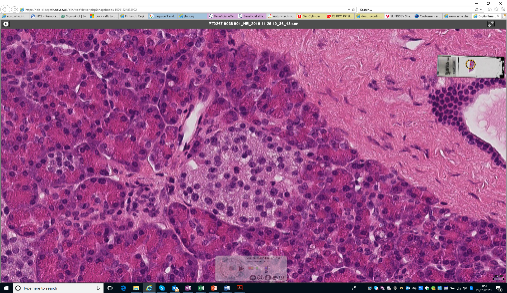
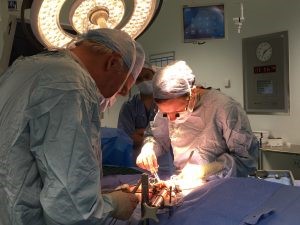
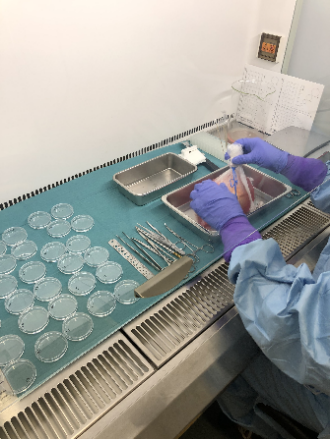
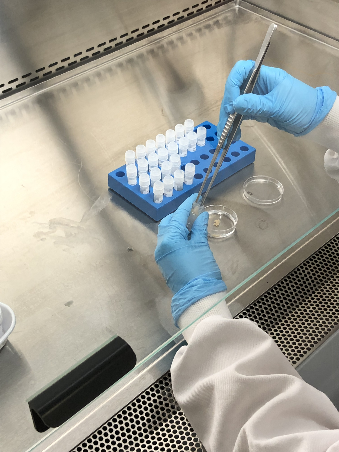
Following dissection from surrounding tissue, the whole organ is assessed and photographed macroscopically prior to collection of multimodal biopsies from anatomically defined regions. Light microscopy images are obtained following a standard suite of dye and immunohistochemical stains for clinical pathologist assessment and artificial intelligence-driven image analysis (led by Professor Sarah Richardson, Exeter University). Standardised ultrastructural assessment by transmission electron microscopy has been validated.
The whole organ expansion programme has benefitted significantly from an NHSBT initiative, Increasing the Number of Organs Available for Research (INOAR), which has included pancreata from donors with diabetes.
The QUOD expansion programme is aligned to the overall QUOD mission ‘Saving lives and cutting health care costs by increasing the pool of transplantable organs, thereby addressing the growing gap between supply and demand in organ transplantation’ and provides a powerful new resource for disease-specific research.
QUOD Panc Atlas
An online Portal is in development providing access to a library comprising donor data; organ / tissue images; AI analysis; and a catalogue of samples available for research within the Quality in Organ Donation whole organ human pancreas tissue bank – QUOD-PANC.
The goal is to establish, curate, and share a unique Bioresource representing the range of normality, acute stress, and chronic disease within human pancreas in parallel with access to detailed donor clinical data and quality-assured clinical pathologist reporting.
Integration with the core QUOD Biobank enables parallel access to donor circulating blood and urine samples in addition to small biopsies from other tissues.
The portal provides access to organ donor clinical data in parallel with macroscopic and microscopic pancreas images. Multimodal samples from each anatomically defined region (8 in total from head to tail of pancreas) comprise formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue blocks (anterior and posterior), snap-frozen tissue blocks, bulk protein samples, RNAlater samples, and glutaraldehyde-fixed samples for EM. Sample details are catalogued for each donor.
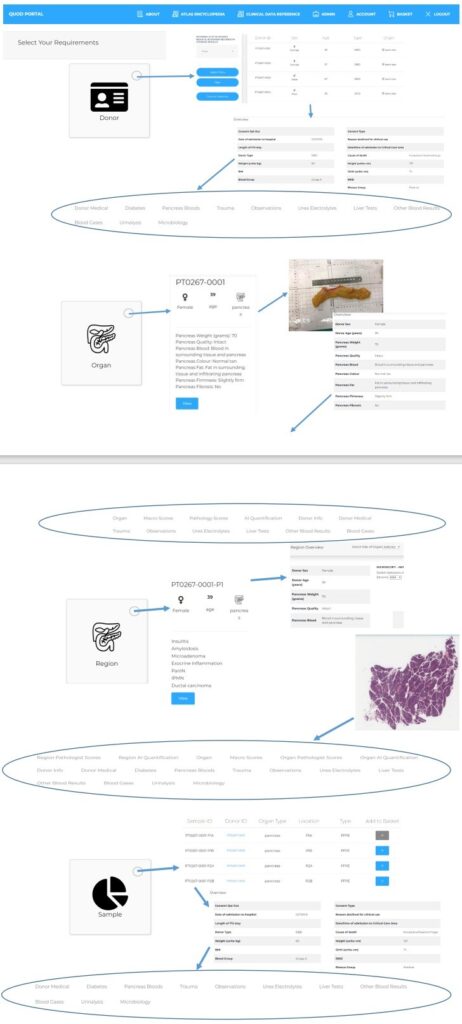
Initial requests can be made through the portal for samples to be processed centrally or released for approved research.
Researchers wishing to access QUOD samples should submit a preliminary registration online for administrator approval and, if successful, submit a relevant project for review.
Contact us at atlasportal@ncl.ac.uk
For further information on the work being undertaken in Newcastle please go to Regenerative Medicine, Stem Cells, Transplantation | Faculty of Medical Sciences | Newcastle University (ncl.ac.uk)



